What’s the Difference Between CBD and THC?
CBD and THC — short for cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol — are two of the most abundant natural chemical compounds in cannabis plants (marijuana and hemp). And with the recent legalization of industrial hemp, you’re probably hearing these terms pop up a whole lot in conversation lately, especially as they relate to physical and mental health. But you probably also have a whole lot of questions.
In a nutshell, both CBD and THC are natural compounds called cannabinoids, but they vary drastically in how they affect the body: THC is psychoactive, intoxicating, and somewhat agitating, while CBD can actually be used to quell anxiety without any trippy effects.
But that description really just scratches the surface. Here, discover more important differences between CBD and THC, their respective therapeutic uses and side effects, and which one is generally the best option for promoting overall health.
Where are CBD and THC found?
CBD and THC are both found exclusively in cannabis plants. In general marijuana plants are high in mind-altering THC and low in CBD, which is why people smoke it to get high. Industrial hemp, on the other hand, is high in anxiety-easing CBD and low in THC, which is why you see a many hemp-derived CBD oils, vapes, and gummies hitting the market. By law, industrial hemp must contain less than 0.3% THC content.
How do CBD and THC Affect the Body?
Despite the fact that CBD and THC are both considered cannabinoids, they are totally different in the way make you feel — to the point that some experts argue THC shouldn’t even be lumped into the cannabinoid category. That’s because, unlike CBD and the dozens of other cannabinoids present in cannabis, THC has a very different effect on our body’s endocannabinoid system.
The relationship between CBD, THC, and the endocannabinoid system is a little complicated, so first, we’ll explain what the endocannabinoid system is…
CBD influences a variety of other processes that help your body’s own cannabinoids bind to their receptors more effectively, thus subtly enhancing the entire endocannabinoid system.
The endocannabinoid system is an offshoot of the endocrine system (or the hormone system) that helps regulate nearly every other system in the body. It consists of a series of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors, which can be found all over the body, including the brain, GI tract, heart, and reproductive system. Its influence is vast, which is why some people refer to it as our body’s master regulatory system.
Some cannabinoids are naturally produced within the body, which bind to cannabinoid receptors to make all of our other bodily systems function more optimally—these are endocannabinoids. Other cannabinoids, including THC and CBD, are produced by cannabis plants, and they influence our endocannabinoid system whenever we smoke marijuana, take CBD or cannabinoid-rich oil, or use any other marijuana- or hemp-derived product.
But how exactly does THC interact with the endocannabinoid system compared to CBD and other cannabinoids? It all has to do with receptors...
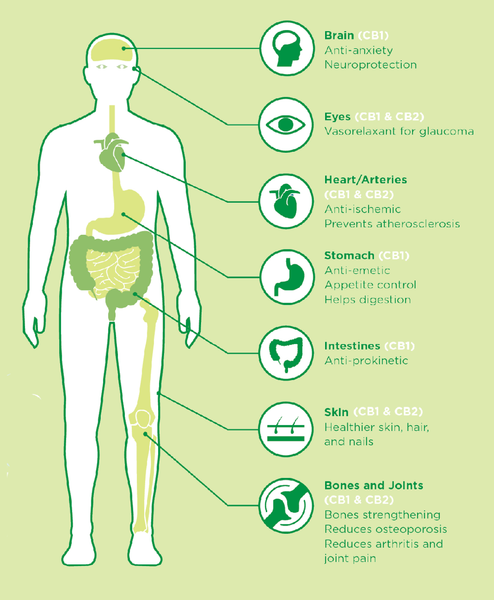
Research has identified two specific types of cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors (sometimes called anandamide receptors) are found mostly in the brain, where they affect functions such as cognition, memory, motor movements, and pain perception. CB2 receptors are located all over the body, including the nervous, immune, and GI systems.
THC binds to and activates CB1 receptors (like a lock and key) and results in the altered state of mind, paranoia, and sleepiness someone may experience when they consume THC. This direct binding and activation of CB1 receptors is why THC has such a potent, drug-like effect. CBD, on the other hand, primarily targets CB1 and CB2 receptors — but in an indirect way. Instead of acting like a lock and key, CBD influences a variety of other processes that help your body’s own cannabinoids bind to their receptors more effectively, thus subtly enhancing the entire endocannabinoid system. This triggers a wide range of physical and mental perks, but without any intoxicating effects. Win-win.
What are the Health Benefits + Side Effects of CBD?
Because CBD helps enhance the functioning of the endocannabinoid system as a whole, it makes sense that it would deliver a variety of head-to-toe benefits — and preliminary research is beginning to back up this theory. Here are some of the most promising CBD perks to date:
- It reduces the frequency of seizures in epileptic patients. It also seems to help ease seizure disorders and anxiety in dogs.
- It helps alleviate symptoms of anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorder, and PTSD.
- It boosts overall brain health by preventing free radical damage, reducing inflammation, and protecting brain cells; and by stimulating the growth of new brain cells.
- It helps reduce pain throughout the body, due in part to its anti-inflammatory activity. One study found that topical application of CBD reduced osteoarthritis-related joint pain.
- It improves digestive health, with research suggesting it may help heal leaky gut and reduce symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases such as IBS.
- It may slow the growth of cancer, according to preliminary lab and animal studies.
Even better, there are practically no side effects of taking CBD. Typically, the only reported side effect is a little bit of digestive upset or nausea, but that’s definitely not the norm. In fact, the Word Health Organization recently issued a report stating that CBD doesn’t appear to have negative side effects or cause addiction.
What are the Health Benefits + Side Effects of THC?
THC’s benefits have been somewhat overblown throughout the years, and research is beginning to reveal that CBD is much more beneficial for overall health, especially when combined with other cannabinoids and terpenes in a full-spectrum hemp product. That said, there are a few key ways THC can be helpful:
- It helps ease neurological (or nerve) pain, e.g. sciatic nerve pain.
- It stimulates appetite in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- It may help manage symptoms of glaucoma by reducing intraocular pressure in the eyes.
However, unless you have a specific need for medical marijuana or another THC-containing product, you may want to steer clear of THC. That’s because THC side effects often outweigh their benefit. Too much THC can cause increased heart rate, dizziness, vomiting, anxiety, sleepiness, paranoia, lack of coordination, and difficulty learning or forming memories.
These negative effects can even be severe enough to prompt people to go to the emergency room. According to National Institute on Drug Abuse, regularly exposing your body to too much THC can also cause dependence or addiction, and people who use marijuana or other high-THC products frequently often report withdrawal symptoms after quitting.
CBD, THC, and the Entourage Effect
Right now CBD probably sounds pretty great, right? But while it’s often touted as the main health-promoting component of cannabis, the truth is, many other cannabinoids exist that are beneficial. In fact, when a variety of cannabinoids are present at the same time, they actually boost the effectiveness of each other. Meaning, an oil, vape, or topical that simply contains one cannabinoid, like CBD, would be far less beneficial than one containing a variety of cannabinoids like CBD, CBC, CBG, and CBN. This synergy between cannabinoids and some other cannabis compounds (like terpenes ) is known as the “entourage effect.”
Contrary to popular belief, THC is actually not necessary for the entourage effect to occur. Because THC acts on the body in a completely different way than other cannabinoids, it plays no role in enhancing how those cannabinoids function in the body. Many people assume that a little THC is necessary to “unlock” the benefits of CBD, but this simply is not true.
Bottom Line: For the average person, THC is kind of overrated from a health-boosting perspective, CBD is more beneficial than THC, and a cannabinoid-rich, THC-free product (like any of the ones from TruestYou) featuring CBD along with range of other cannabinoids and terpenes is the best of all.
—————————————————
Written by health coach and wonderful human being, Steph Eckelkamp. Check out some of her other informative articles on her website.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease, and has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
